Mid-September is a time when everyone gets used to the idea that the holidays are over and colder days are coming. However, this does not apply to the financial market, as autumn is usually a period of greater volatility than the summer months. Ethereum, for example, has used half of this month to take a daring step in the development of the chain, which was supposed to increase its efficiency and reduce costs.
What was The Merge?
September 15, 2022, marked a pivotal moment in the history of Ethereum and blockchain technology as a whole. On this day, the blockchain completed The Merge, a highly anticipated upgrade in which the network transitioned from the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus algorithm to Proof of Stake (PoS). This move was designed to reduce the network’s energy consumption significantly and lay the groundwork for better scalability and sustainability in the long term.
Before The Merge, Ethereum relied on Proof of Work, a mechanism in which miners competed to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. This process, while secure, was energy-intensive and environmentally unsustainable. Ethereum’s move to Proof of Stake meant that instead of miners using computational power, validators now stake their Ether (ETH) to gain the right to validate transactions and propose new blocks. This made the network far more energy-efficient and reduced the need for large-scale hardware, lowering the entry barrier for participation in securing the network.
The transition to Proof of Stake led to an estimated 99.95% reduction in Ethereum’s energy consumption, a significant achievement in a world increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of blockchain technologies. This shift was part of a larger vision called Ethereum 2.0, aimed at improving the network’s performance and sustainability.
Sounds good?
The ETH Merge: Market reaction
The market is the final judge of any change, whether at the enterprise level or in cryptocurrencies, with a clearly defined management team. So, let’s look at the project’s valuation after more than two years.
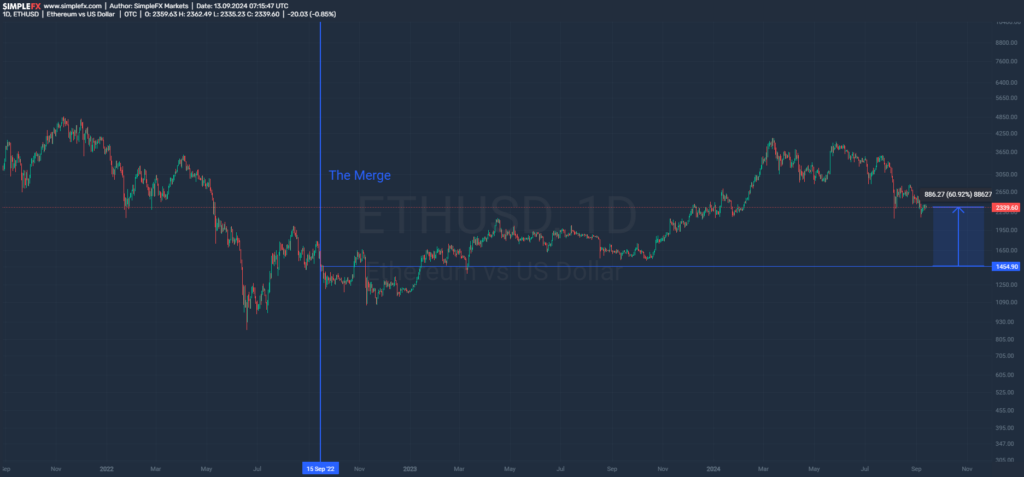
ETHUSD 2 years after The Merge.
As you can see, initially, The Merge was a typical sell-the-news event. However, it should be added that it occurred in the late phase of the 2022 bear market, where the market was already oversold, and the ETH price dropped from approximately $4,800 to $1,454 (-70%). Further increases may, therefore, be not only the result of technological change but also a general movement resulting from cryptomarket cyclicality. So, how can we cleanse this data?
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin: A plummeting ETH/BTC ratio
Just as the benchmark in the TradFi world is most often the S&P500 index, for cryptocurrencies, it is always Bitcoin. The oldest currency that sets trends and market cycles. To succeed in the crypto market, you must at least maintain its growth rate and preferably beat it.
This is measured by a simple quotient that shows how many pieces of BTC should be paid for one piece of the selected altcoin. If this coefficient is constant, the rise and fall of a given pair are exactly the same. If this pair grows, the altcoin gains relatively. When it falls, the altcoin loses to BTC.
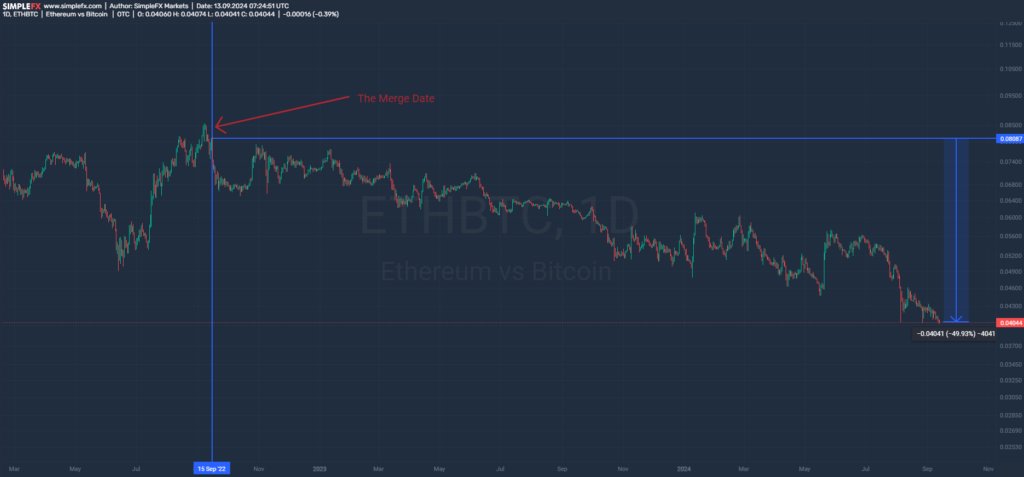
ETHBTC: Road to Hell
Despite the technical success of The Merge, Ethereum has faced a decline in value relative to Bitcoin (ETH/BTC) over the last two years. Today, Vitalik’s altcoin has lost almost 50% of its value against Bitcoin since The Merge. What does it look like from a technical perspective?
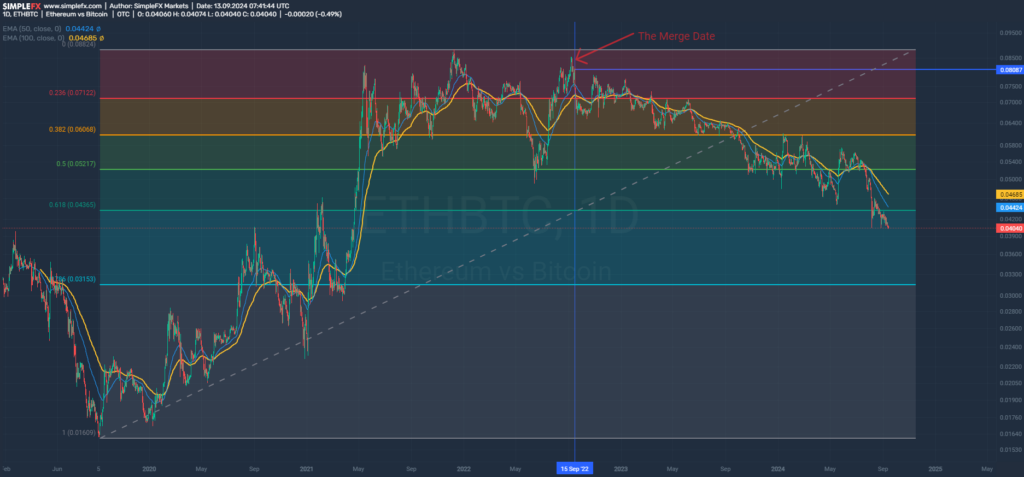
ETHBTC high-time frame.
For now, mid-September 2022 marks a multi-year peak for this pair. Ethereum not only lost half of its value compared to Bitcoin in just two years but also broke almost all FIBO supports determined from the pair’s low from precisely five years ago. The price is below EMA50 and EMA100, which also formed a death cross at the end of July. The last unbroken Fibo support remains at the level of ~0.03.
The Merge: What might went wrong?
Well, a lot. Despite its significance for Ethereum, The Merge wasn’t without its challenges. While it marked an essential transition from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake, several issues have contributed to the declining ETH/BTC ratio and overall market sentiment.
Lack of Immediate Benefits for Users
While The Merge was an essential milestone for Ethereum, it did not bring immediate, tangible benefits to everyday users. High gas fees and network congestion remain prevalent during periods of high demand. The Merge did not directly address these issues, which are crucial for those using decentralized applications (dApps) on Ethereum. Until further upgrades, Ethereum’s scalability problems persist, causing some users and investors to look elsewhere for more cost-effective solutions.
Competition from Layer 2 Solutions and Other Blockchains
Although Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake is a long-term play for network scalability, it still faces stiff competition from both Layer 2 (L2) solutions and alternative blockchains. Competitors like Solana, Avalanche, and Cardano have emerged with lower fees and faster transaction times, offering users an attractive alternative. At the same time, Layer 2 scaling solutions built on Ethereum, such as Arbitrum and Optimism, are gaining traction. These networks alleviate Ethereum’s congestion by handling transactions off-chain but still present competition for user adoption and transaction fees.
This rivalry affects Ethereum’s short-term performance and perceived value compared to Bitcoin, which enjoys a “safe-haven” status among cryptocurrencies due to its long-standing dominance and role as “digital gold.”
Centralization Concerns
One of the criticisms surrounding Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake is the potential centralization of staking power. In Proof of Stake, validators are selected to propose and validate new blocks based on the amount of ETH they have staked. This can lead to situations where large institutions or centralized entities, such as major exchanges, control a significant portion of staked ETH, posing a risk to Ethereum’s decentralization ethos. Currently, a substantial percentage of Ethereum’s staked funds are controlled by a few large players, raising concerns about network centralization and governance.
Macroeconomic Factors and Bitcoin’s Dominance
Global macroeconomic conditions have also contributed to ETH’s decline relative to Bitcoin. With persistent inflation, elevated interest rates, and general market uncertainty, risk-averse investors have gravitated towards Bitcoin, viewing it as a safer asset within the cryptocurrency space. Bitcoin’s status as the first and most established cryptocurrency makes it more resilient in bear markets than altcoins like Ethereum, which are still viewed as higher risk by many institutional and retail investors.
What’s Next for Ethereum?
Despite the short-term struggles in ETH’s price performance, currently, Ethereum remains a foundational layer of the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem and non-fungible token (NFT) market. The Merge laid the groundwork for future upgrades, encompassing scalability issues and lower transaction fees, making it more competitive with alternative blockchains and Layer 2 solutions.
The network’s long-term success might depend on its ability to implement these upgrades and maintain its role as the leading platform for decentralized applications. While the short-term market dynamics may seem unfavorable, Ethereum’s long-term potential remains significant, particularly as a pioneer in PoS and decentralized technologies.
The Merge was a critical step forward for Ethereum, but the network is still navigating challenges, particularly regarding user experience, competition, and market perception. The coming years will be crucial in determining whether Ethereum can fully capitalize on the promises of Ethereum 2.0 and regain its value relative to Bitcoin.
The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute investment advice; instead, all information, content, and materials available on this site are for general informational purposes only.